Cowpea in Orbit: The Success of ISRO's CROPS Mission
Context:
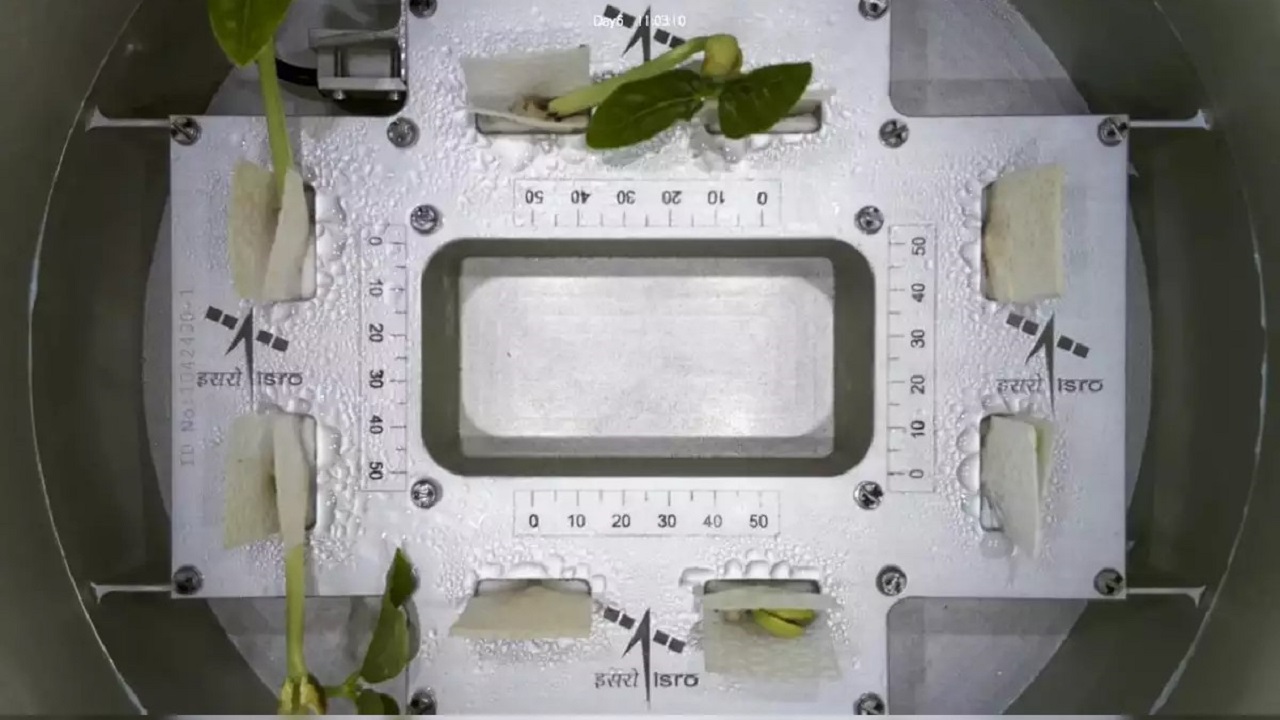
India’s space agency, ISRO, has reached a remarkable milestone in space agriculture through its Compact Research Module for Orbital Plant Studies (CROPS) experiment. Launched aboard the PSLV-C60 mission, this experiment demonstrated the successful germination of cowpea seeds in space, providing critical insights into plant biology in microgravity. This achievement is crucial for addressing challenges related to food security during long-term space exploration.
Key Highlights of ISRO’s CROPS Mission:
-
What is the CROPS Mission?
- Developed by the Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre (VSSC), the CROPS mission aims to develop technology for growing and sustaining plants in space and other extraterrestrial environments.
- The mission is part of ISRO’s larger goal to enable sustainable living in space, especially for long-duration missions to places like Mars.
-
Successful Germination of Seeds in Space:
- Launch Date: The experiment was launched on December 30, 2024, aboard ISRO's PSLV-C60 mission.
- Setup: The seeds were housed in the POEM-4 platform, which is a modified stage of the PSLV rocket designed for scientific research.
- Results: In just four days, eight cowpea seeds successfully sprouted their first leaves, proving that plant growth is possible in space.
Significance of the CROPS Mission:
-
Understanding Microgravity Effects on Plants:
- The experiment helps scientists study how plants adapt and grow in microgravity, a unique condition where gravity is extremely weak, as experienced in space.
-
Supporting Future Space Missions:
- For deep-space missions like those to Mars, astronauts need reliable food sources. This experiment provides a starting point for developing sustainable agricultural systems in space.
-
Advancing Space Agriculture Research:
- The successful growth of cowpea seeds adds valuable knowledge to astrobotany (the study of plants in space), enabling future efforts to grow food in environments beyond Earth.
-
Broader Implications:
- The CROPS mission highlights collaboration between ISRO, academic institutions, and private players, advancing space research and innovation.
Future Applications:
- Ensuring Food Security in Space:
- With missions to Mars and beyond requiring long-term food solutions, experiments like CROPS pave the way for developing sustainable farming systems in space.
- Preparing for Human Settlements Beyond Earth:
- The knowledge gained from this mission will help humanity prepare for establishing colonies on Mars or other celestial bodies.
What is the POEM-4 Platform?
The PSLV Orbital Experiment Module (POEM)-4 is an innovative platform that uses the spent fourth stage of the PSLV rocket for conducting experiments in microgravity.
-
Key Features of POEM-4:
- It is part of the ISRO SpaDeX Mission and is the fourth version of the POEM platform, with three times the capacity of its predecessor.
- It hosts 24 payloads from ISRO, private start-ups, and academic institutions.
-
Notable Experiments on POEM-4:
- Walking Robotic Arm (RRM-TD): A robotic arm that moves like an inchworm to assist with inspections and maintenance.
- Debris Capture Robotic Manipulator: Designed to manage space debris for a cleaner space environment.
- Gradient Control Reaction Wheel Assembly (RWA): A payload to enhance the stability of the POEM platform.
What is the SpaDeX Mission?
The SpaDeX mission is a cost-effective technology demonstration by ISRO to showcase in-space docking technology, where two spacecraft connect while in orbit.
- Importance of In-Space Docking:
- This capability is critical for missions like Moon sample returns, establishing the Bharatiya Antariksh Station (BAS), and future Mars missions.
- Through SpaDeX, India aims to become the fourth country in the world to achieve operational docking technology.
Conclusion:
ISRO’s CROPS experiment marks a significant step forward in space research, showcasing India’s ability to tackle the challenges of long-term space exploration. The successful germination of cowpea seeds aboard the PSLV-C60 mission provides hope for developing sustainable agriculture systems in space. This milestone not only contributes to deep-space mission readiness but also enhances global efforts in growing food beyond Earth. ISRO’s innovative approach and collaborations continue to propel India toward a leadership role in space exploration.
.jpg)
_(10).jpg)

Comments (0)