India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC): A Game-Changer in Global Economic Partnerships
Context
The India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC) is poised to redefine global trade and connectivity by establishing direct trade routes across three continents. Former U.S. President Joe Biden emphasized its potential during discussions following the Israel-Hamas ceasefire, highlighting its strategic importance in fostering regional cooperation and economic growth.
This corridor emerges against a backdrop of shifting global dynamics where nations seek sustainable, efficient, and inclusive frameworks for economic integration. With its origins rooted in multilateral agreements, IMEC signifies a step toward a more interconnected and resilient global economy.
What is IMEC?
1. Introduction:
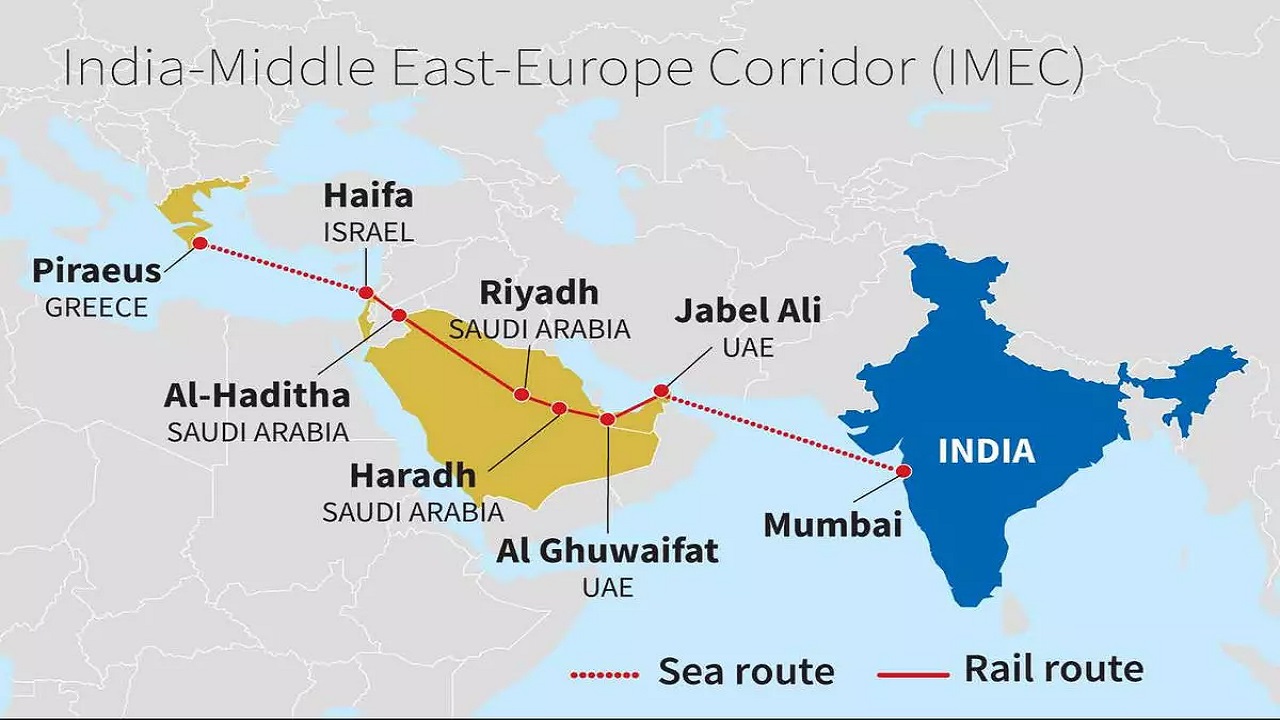
IMEC is a connectivity initiative designed to enhance trade and infrastructure between India, the Arabian Peninsula, the Mediterranean region, and Europe.
-
Key Announcement:
IMEC was launched during the G20 Summit in New Delhi (2023), where a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) was signed by the European Union and seven countries:
India, the U.S., Saudi Arabia, UAE, France, Germany, and Italy. -
Structure:
- Eastern Corridor: Links India to the Arabian Gulf.
- Northern Corridor: Connects the Arabian Gulf to Europe through the Mediterranean.
2. Core Components:
- Shipping routes: Connect ports in Mumbai and Mundra (Gujarat) with the UAE.
- Railways: Link the UAE, Saudi Arabia, Jordan, and the Israeli port of Haifa to the Mediterranean.
- Maritime links: Extend from Haifa to Piraeus, Greece, and onward to Europe.
- Energy and Digital Infrastructure: Includes pipelines for hydrogen, electricity grids, and optical fiber networks for enhanced connectivity.
Strategic Objectives
1. Economic Integration:
- Creation of cost-effective trade routes reducing reliance on chokepoints like the Suez Canal.
- Faster movement of goods, unlocking untapped trade potential for inland and underdeveloped regions.
2. Strategic Counterbalance to China’s BRI:
- Unlike the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), which has faced criticism for debt dependency, IMEC promotes:
- Market-driven investments
- Democratic principles
- Equitable partnerships
- Enhances India's global economic standing by positioning it as a central player in international trade.
3. Energy and Technological Advancement:
- Supports green energy goals with hydrogen pipelines and renewable energy initiatives.
- Develops high-speed digital networks, fostering innovation in AI, fintech, and cybersecurity.
4. Geopolitical Significance:
- Strengthens ties between participating nations, enabling Middle Eastern nations to modernize and Europe to deepen relations with South Asia.
Key Benefits of IMEC
- Efficiency: Reduces transportation costs and increases trade accessibility.
- Sustainability: Promotes renewable energy and reduces greenhouse gas emissions.
- Economic Growth: Boosts employment opportunities and strengthens supply chains.
- Innovation: Facilitates technological advancements through integrated digital infrastructure.
Challenges and Opportunities
1. Financial Investments:
- Challenge: The project requires significant funding, balancing national priorities like education and healthcare.
- Opportunity: Attracting private-sector participation through risk-sharing and financial incentives.
2. Political Coordination:
- Challenge: Diverse economic and strategic goals of participating nations.
- Opportunity: Enhanced diplomatic engagements, regular summits, and multilateral negotiations to align priorities.
3. Infrastructure Development:
- Challenge: Uniform construction standards across nations and mitigating bureaucratic hurdles.
- Opportunity: Collaboration among leading engineering firms and technology providers to ensure efficiency.
4. Balancing Sustainability with Growth:
- Challenge: Transitioning to clean energy infrastructure in fossil-fuel-dependent regions.
- Opportunity: Leveraging partnerships with green energy leaders like India and Germany to accelerate adoption.
The Role of U.S. Leadership
The U.S. plays a critical role in IMEC’s success:
- Strategic Support: Builds on frameworks like the Abraham Accords, fostering Middle Eastern cooperation.
- Diplomatic Influence: Consolidates partnerships with key players like India, Saudi Arabia, and the EU.
- Visionary Leadership: Positions the U.S. as a driving force in promoting sustainable and equitable global economic frameworks.
Conclusion
The India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor represents a bold vision for transforming global trade and connectivity. By linking diverse economies, enhancing technological innovation, and prioritizing sustainability, IMEC has the potential to:
- Reshape global trade routes.
- Foster regional stability and cooperation.
- Address pressing global challenges like climate change.
With India and the United States leading the charge, IMEC embodies a beacon of collaborative progress for the 21st century, offering an alternative to unilateral and debt-driven initiatives. Its realization will depend on political will, financial commitment, and coordinated execution, but its success could redefine the future of global economic partnerships.



Comments (0)